How to Put Uploaded Files Into a Folder Javascript
A Complete Guide to File Uploading in JavaScript
Single file, multiple files, drag, and paste, everything yous demand to know

File upload is a common part for a web project. I believe that everyone has encountered related requirements more or less during the development.
In this article, I have summarized some scenarios and solutions, hoping to help you lot thoroughly grasp questions related to file uploading.
Our Goals
First, let's analyze the specific functions of file uploading.
According to upload target, at that place are 3 kind tasks:
- Upload a single file
- Upload multiple files at the same time
- Upload the entire binder
According to the user deportment, in that location are:
- Choose a file the upload
- Drag the file to the box and so upload
- Upload from clipboard
From a functioning perspective, we may need:
- Upload later compressing a file
- Divide a large file into blocks and so uploading
And additionally, sometimes nosotros may not upload files in the client browser, merely through the server to upload to another server.
Nosotros will talk over these in turn.
Prerequisites
Earlier the start coding, nosotros still need to empathize some background knowledge.
First, when uploading files, nosotros utilize Axios, the most pop HTTP Library. In actual evolution, nosotros generally don't use XMLHttpRequest directly, and using Axios conforms to the existent development model.
When we discuss uploading files in the forepart-end, if we want to fully understand the relevant principles, we must understand the relevant back-cease code. Here we utilise the Koa to implement our server.
Finally, I hope you lot will take a brief agreement of formdata, we apply this data format to upload files.
Upload a single file
The need to upload a file is too mutual. For case, when you register for Medium, you lot need to upload an avatar.
The file upload role requires cooperation between the client and the server. In our project, the user selects a file in the customer and uploads information technology to the server; the server saves the file and returns the URL of it.
Hither is the project preview:
The above Gif shows the consummate process of file uploading:
- User selects a file in the browser
- User click the upload button
- The uploaded files are placed in the
uploadFilesfolder of the server - So the server returns a URL, which is the address of the uploaded file
- Users tin access the resource through this URL
The Code
All the code of this projection was held on GitHub:
Yous can clone information technology to your computer:
# clone it
$ git clone git@github.com:BytefishMedium/FileUploading.git # and install npm package
$ cd FileUloading
$ npm install
All the code related to unmarried file uploading was put on ane-SingleFile binder.
-
client.htmlrelated to customer-side code. -
server.jsrelated to server-side lawmaking
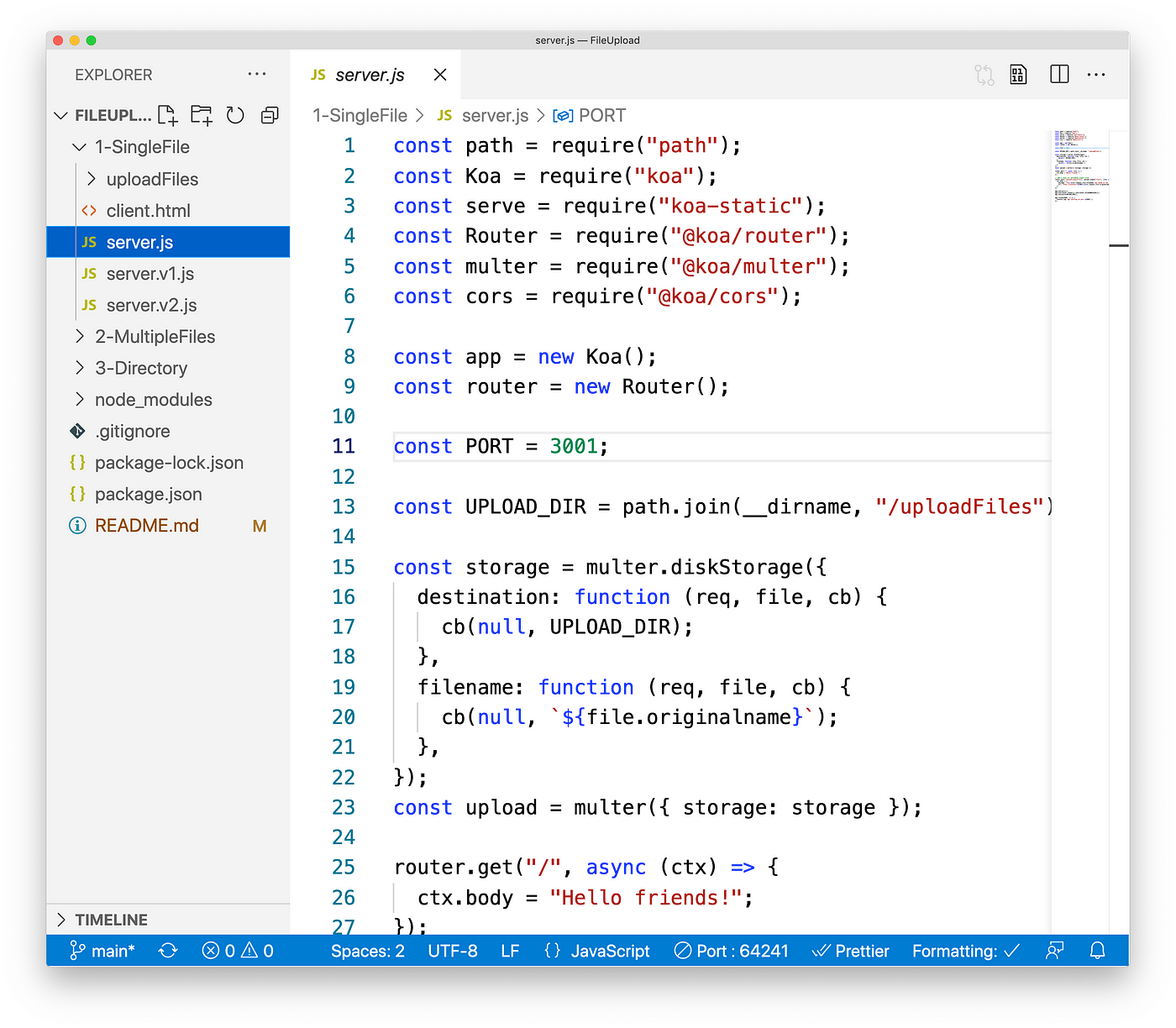
To run the server, you can get to the folder and run this control:
$ node server.js Then y'all can open up client.html on any browser.
The specific operation I have shown in the gif to a higher place. You lot can try it for yourself first, and then read on.
Customer-side code
Um, How many steps does it take to put a giraffe into a refrigerator?
Just three steps:
- Open the door
- put the giraffe in
- and close the door.
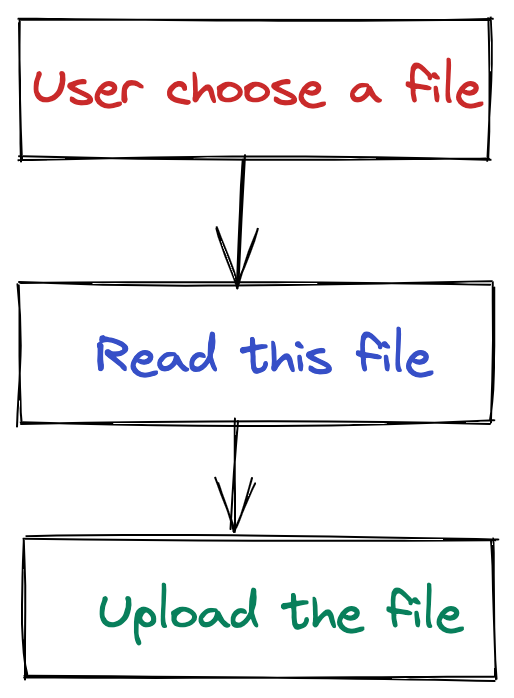
The aforementioned is truthful for uploading files, we merely need three steps:
- Let users choose a file to upload
- Read this file
- Upload the file using Axios
In HTML, we can use the input element. Simply ready the type of this element to file, then the element tin can be used to select the file.
<input id="fileInput" blazon="file"/> 
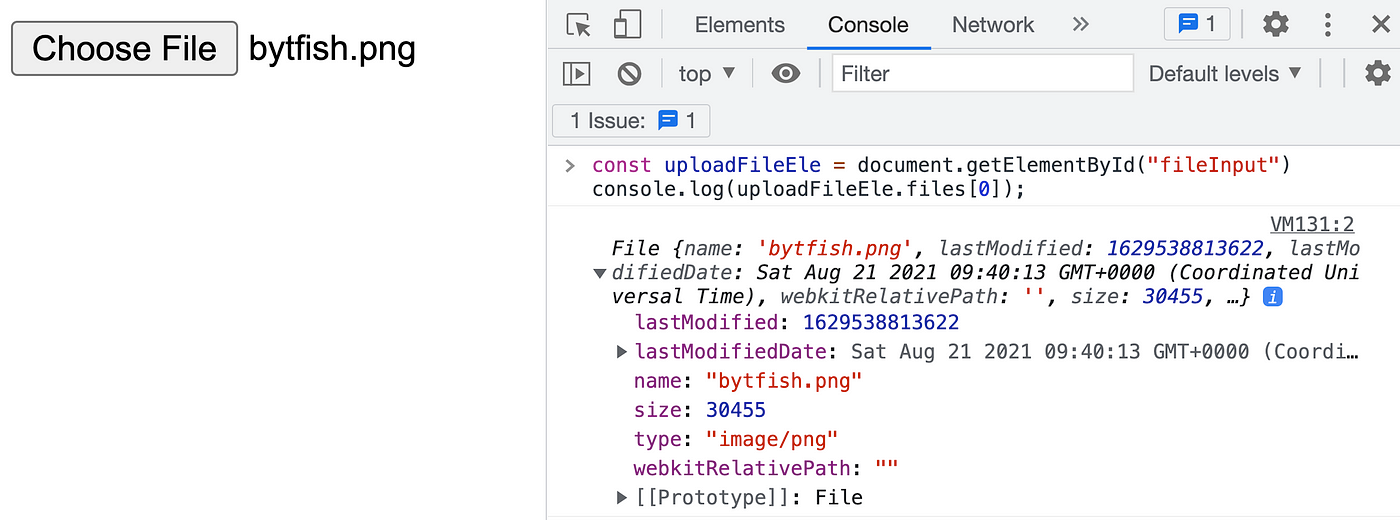
Later the user selects a file, the metadata of the file will be stored in the files property of this input element.
const uploadFileEle = certificate.getElementById("fileInput") panel.log(uploadFileEle.files[0]);
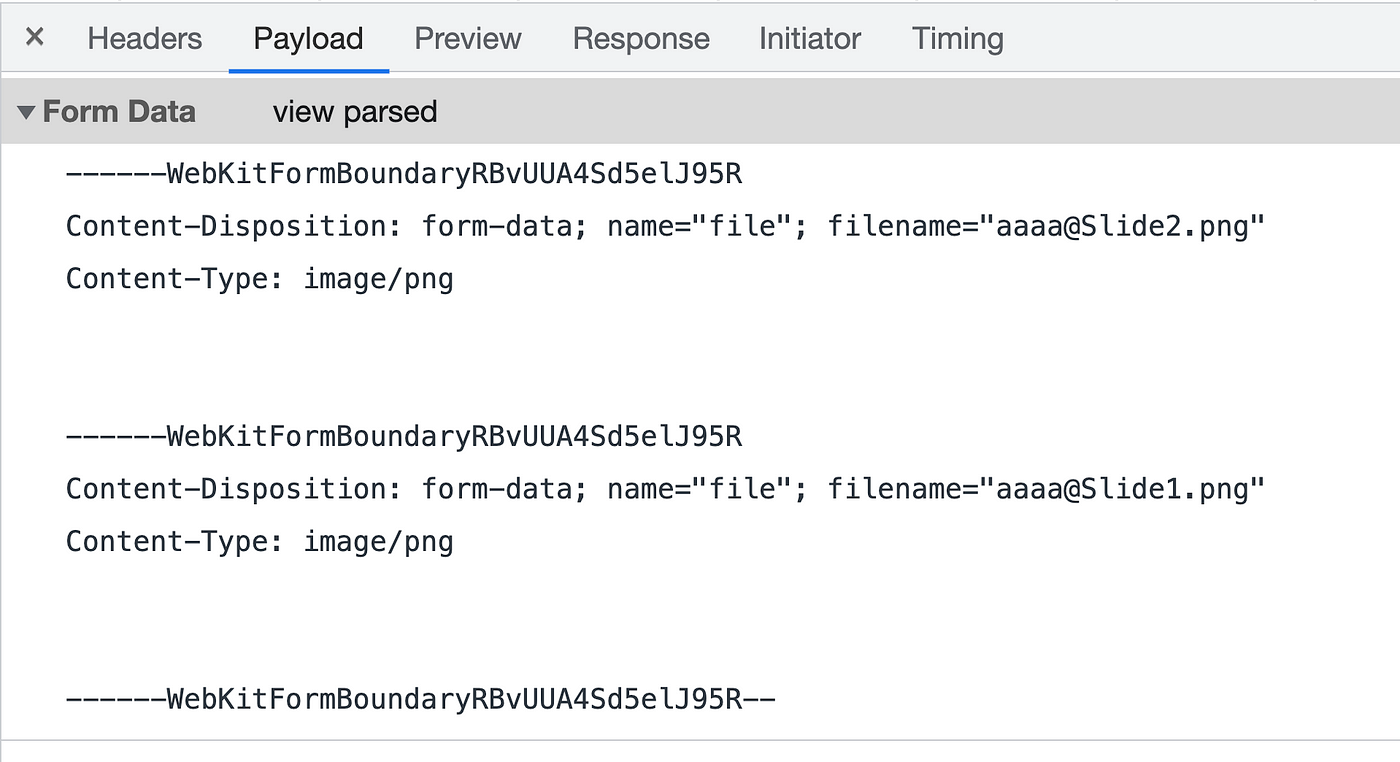
Finally, we use Axios' post method to upload files. But before uploading the file, we also demand to package this file into FormData format.
let file = fileElement.files[0];
permit formData = new FormData();
formData.set('file', file); axios.mail("http://localhost:3001/upload-single-file", formData)
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
Tips: FormData is a cardinal-value blazon information format. Hither is an case:
Well, these are the knowledge points related to file uploading. The more than complete lawmaking is equally follows:
This code is actually to implement the three steps we said before:
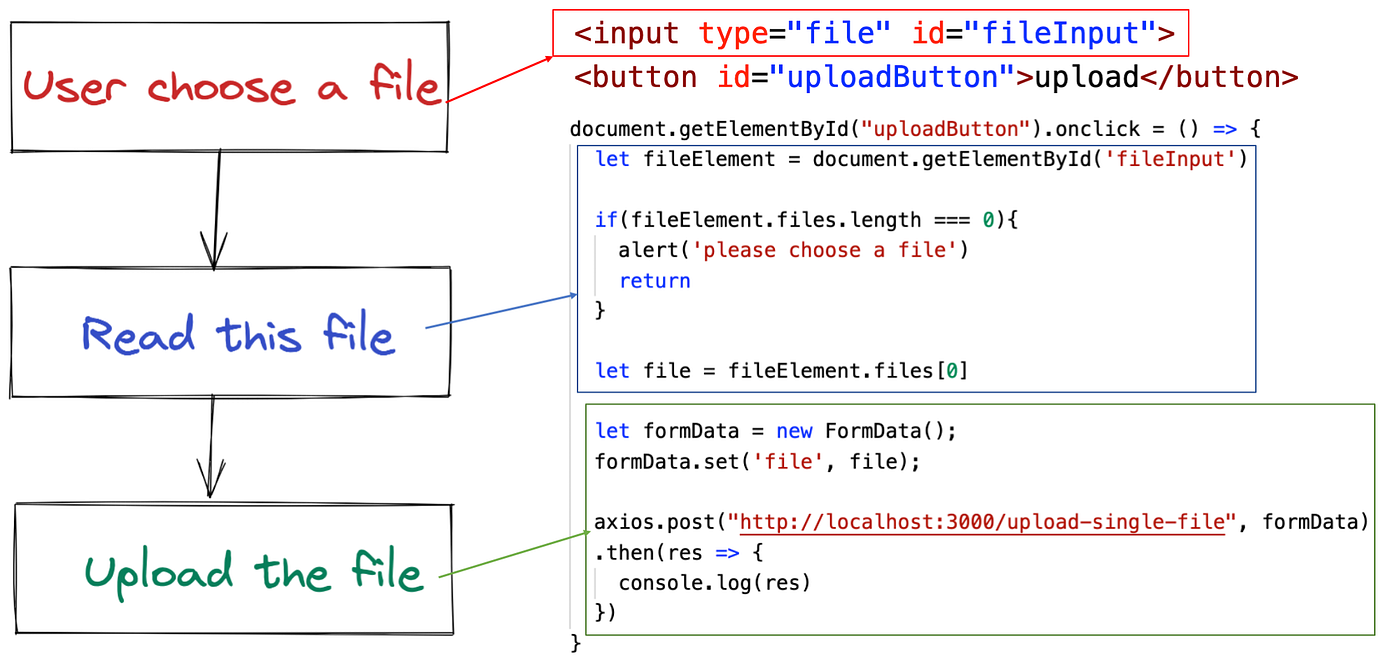
It's only that we added 2 additional functions:
- 1 is the upload button. When the user clicks the upload button, nosotros offset executing the upload logic.
- So we accept 1 more judgment to ensure that the user really selects a file.
And so, when Axios uploads a file, it allows the states to monitor the progress of the file uploading.
We know that HTTP is built on top of TCP. If an HTTP parcel is relatively large, information technology may exist decomposed into multiple different TCP packets for transmissions in the network.
If yous demand to write a progress bar to show the user the progress of the uploading, you can use this API.
axios.post("http://localhost:3001/upload-unmarried-file", formData, {
onUploadProgress: (progressEvent) => {
const percentCompleted = Math.round(
(progressEvent.loaded * 100) / progressEvent.total
);
console.log(`upload process: ${percentCompleted}%`);
},
}); progressEvent.loaded means how many bytes have upload success and progressEvent.full means total bytes of the file.
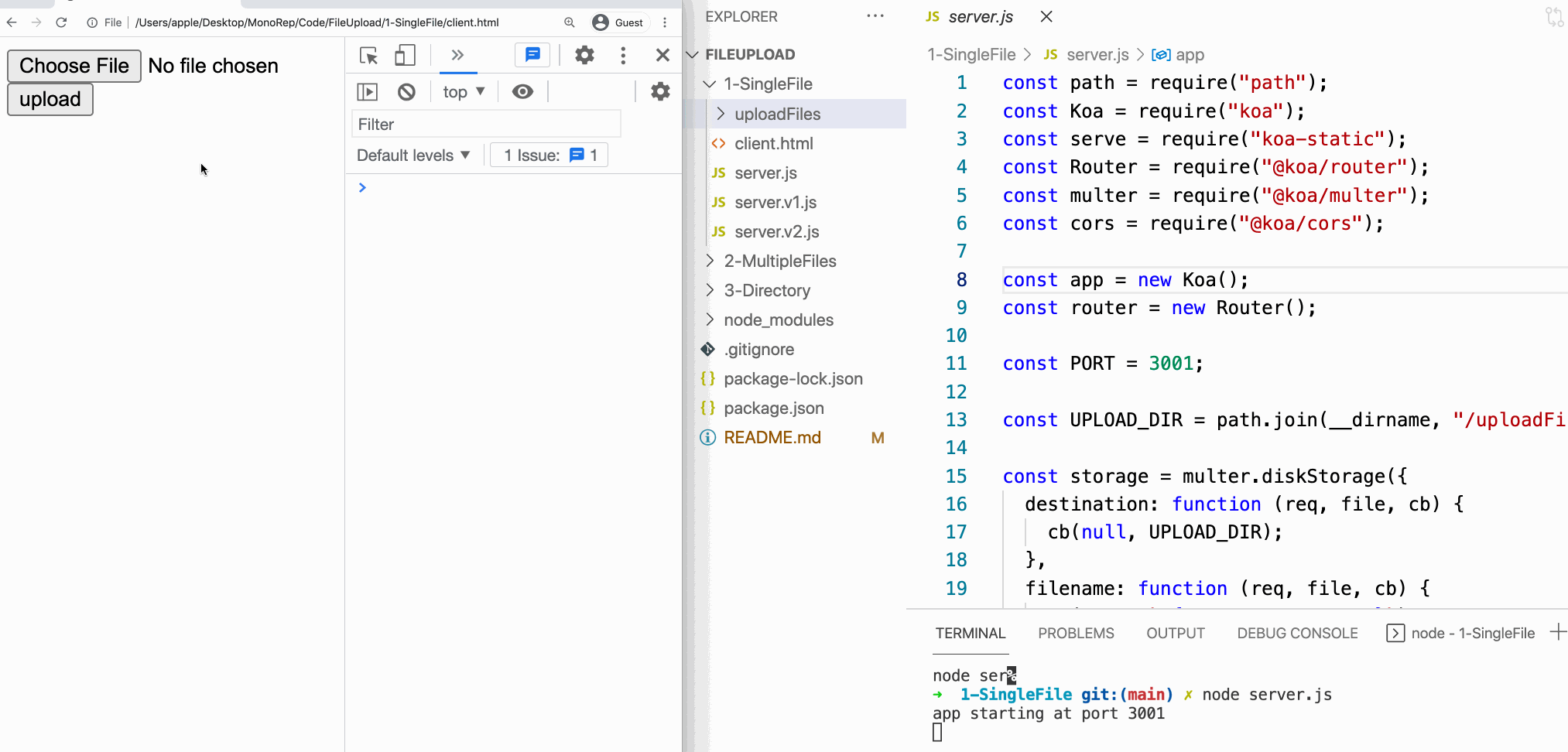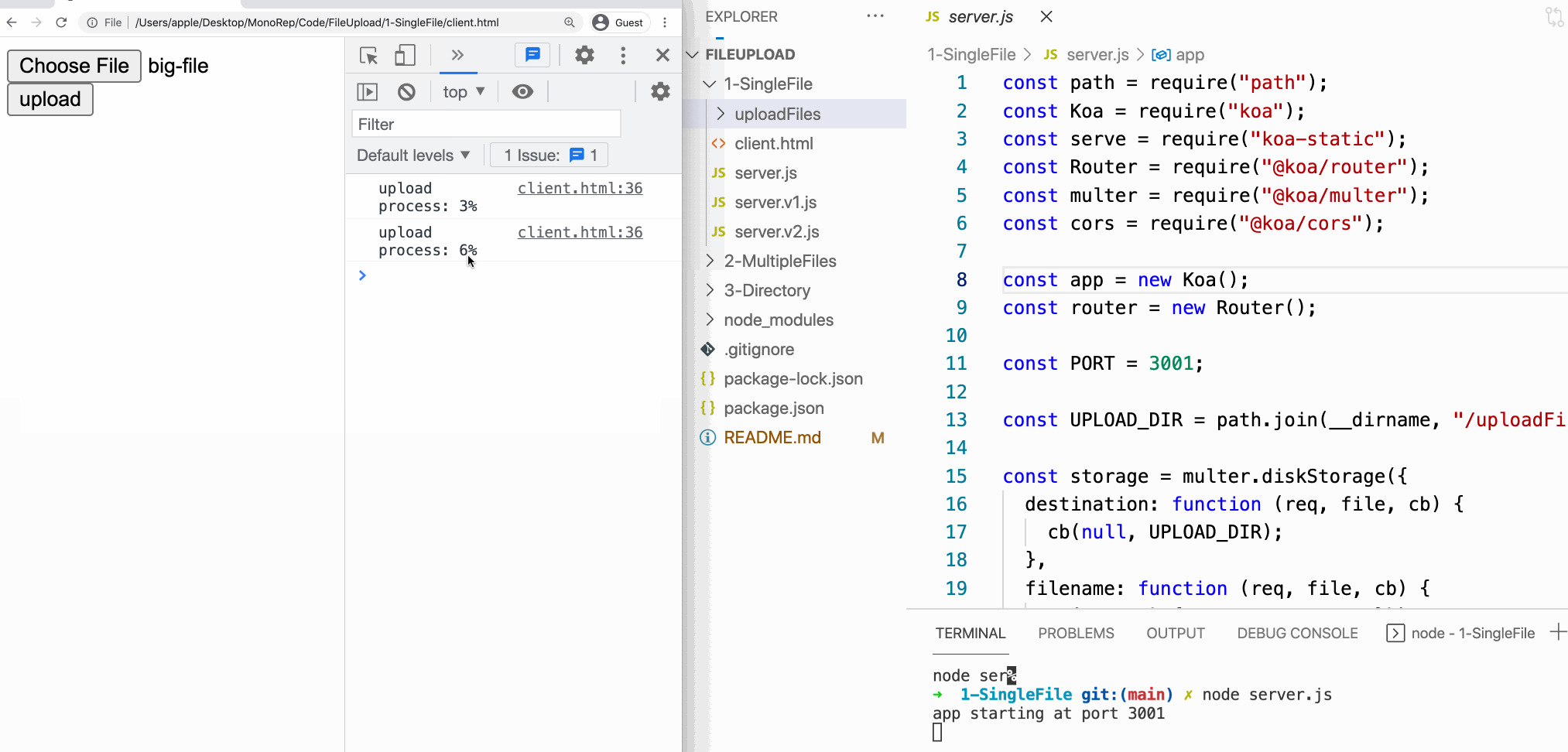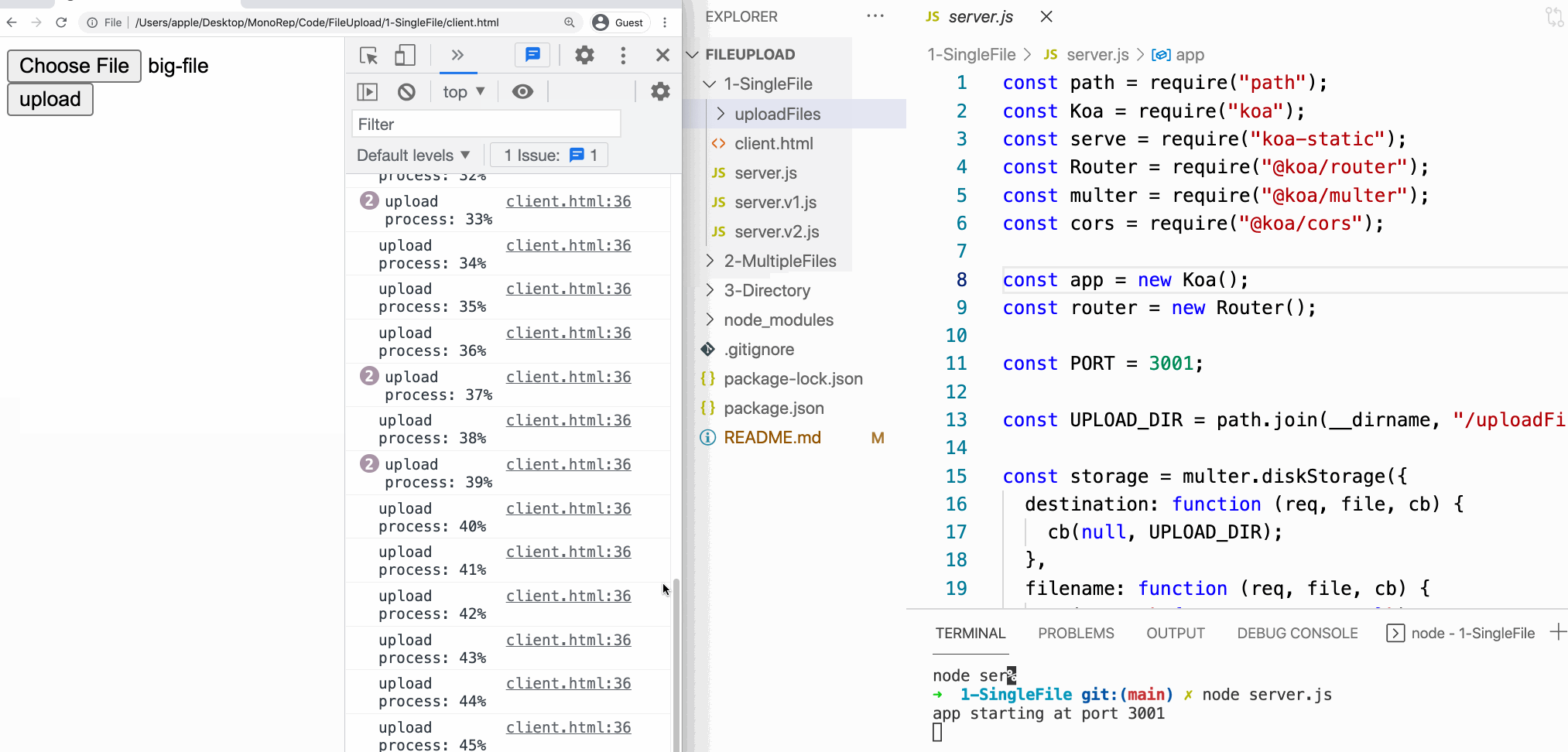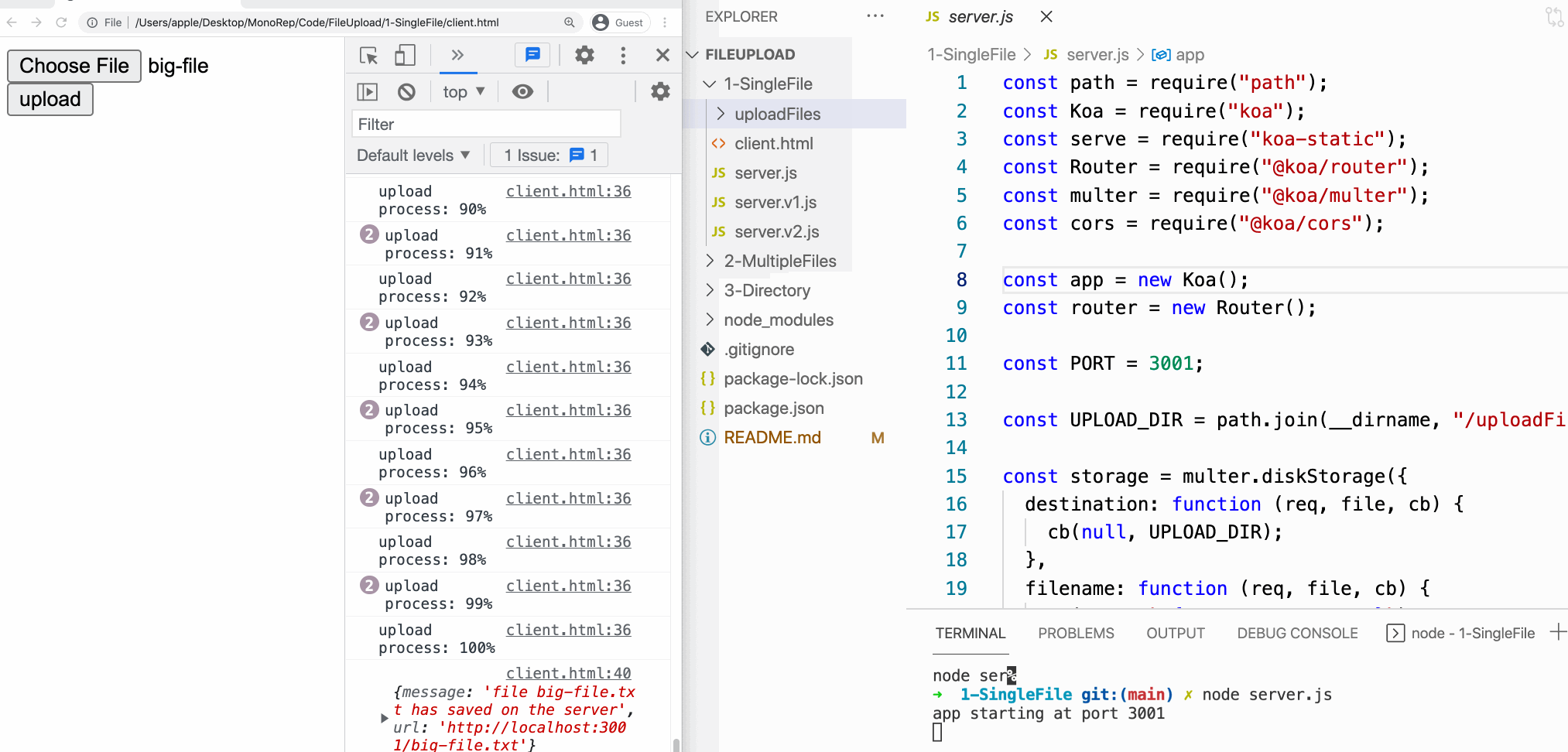
Ok, this is our customer-side code.
Server-side code
To beginning a server, we tin can use Koa. Here is a tiny server using Koa:
This is the near basic Koa demo. Since this article focuses on file uploading, so I will not explicate this in detail. If you don't familiar with this, you can read the official documentation.
- Koa
- Koa-router
Our client uses the format of FormData to upload files, then our server besides needs to parse FormData. And Koa-multer is a middleware that helps us parse FormData data:
About Koa-multer, you can read their official documentation:
- Koa-multer
- Multer
The cardinal lawmaking is uoload.unmarried('file'), this line of code tin can help us parse the data of FormData, and then put the corresponding information in the ctx.request.file.
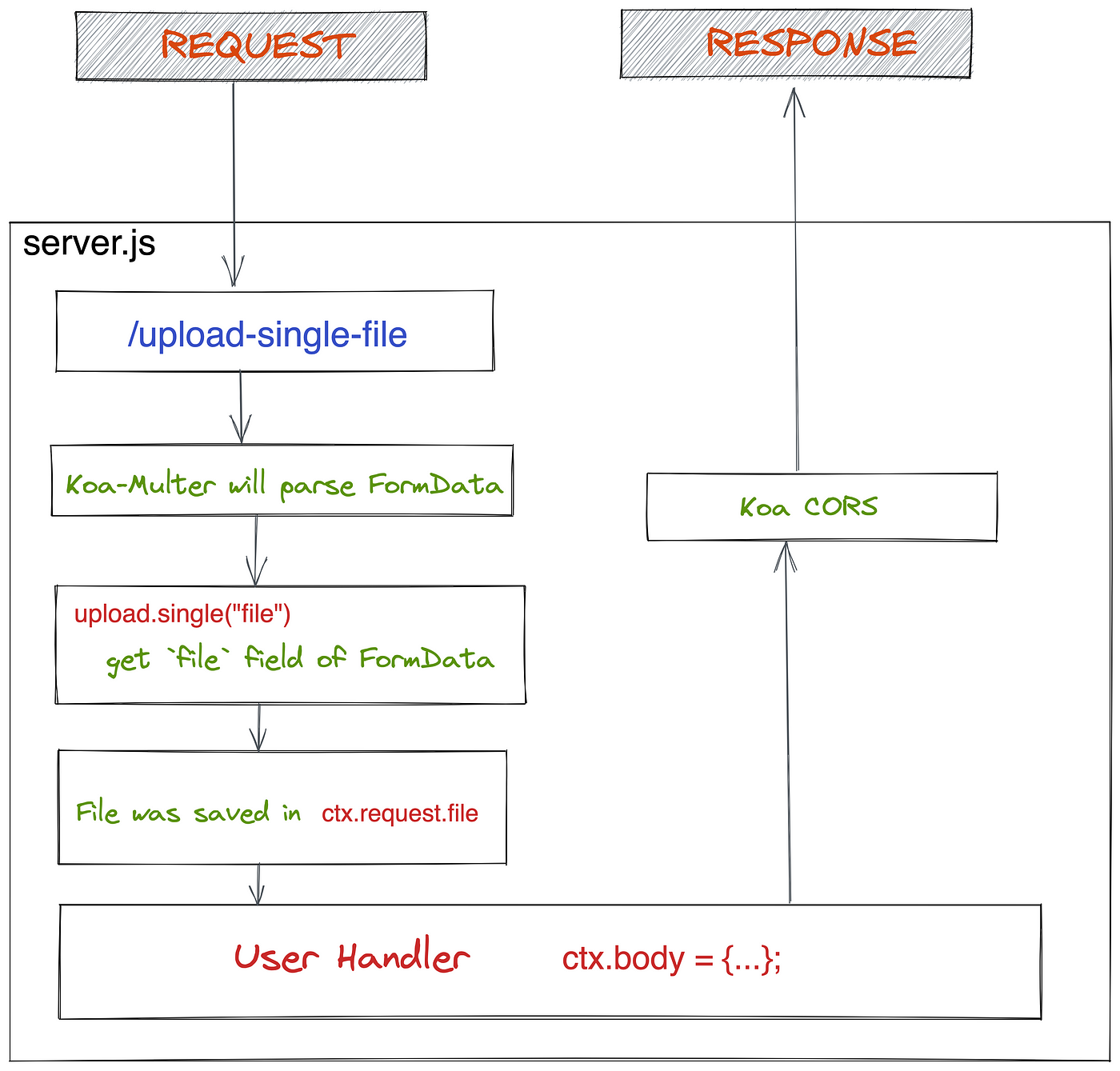
In fact, at this time, our server can already receive the files uploaded by the client, just it does not shop them to the deejay after receiving the files.
If we want Koa-multer to save the file to disk for us, we tin can add the post-obit configuration:
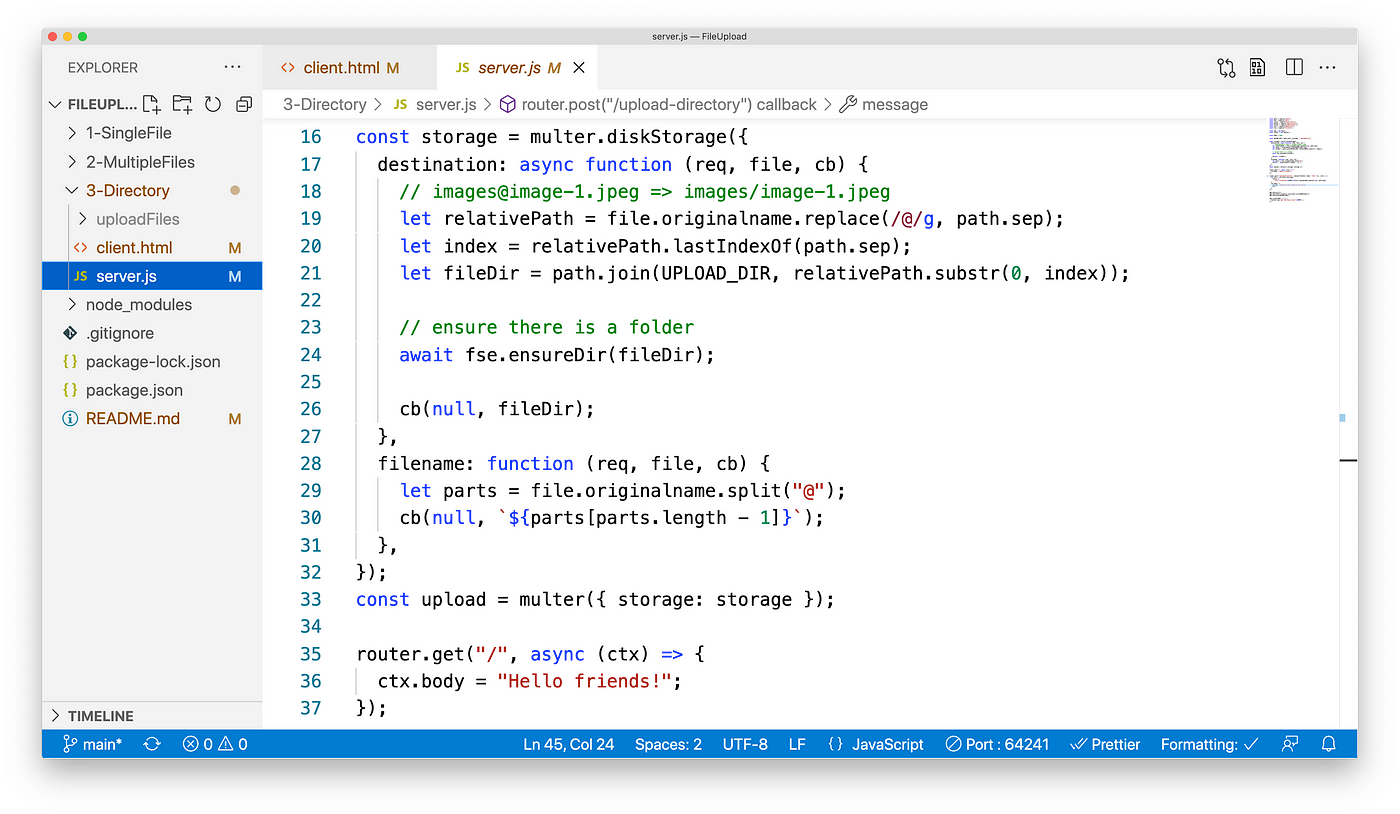
const storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(nil, UPLOAD_DIR);
},
filename: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(null, `${file.originalname}`);
},
});
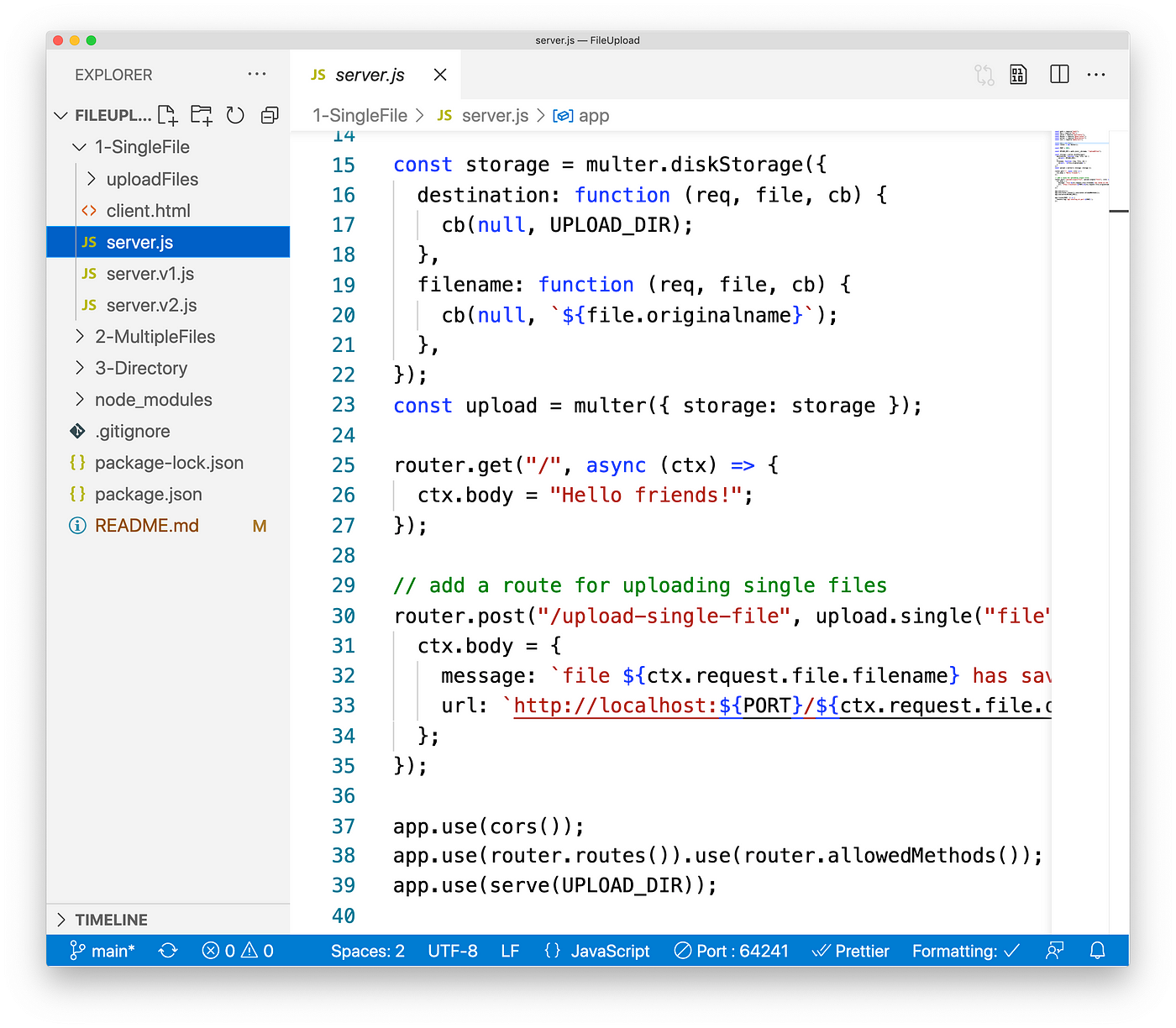
const upload = multer({ storage: storage }); The complete code is server.js, and you can read it directly in the lawmaking repository.
The current flow nautical chart looks like this:
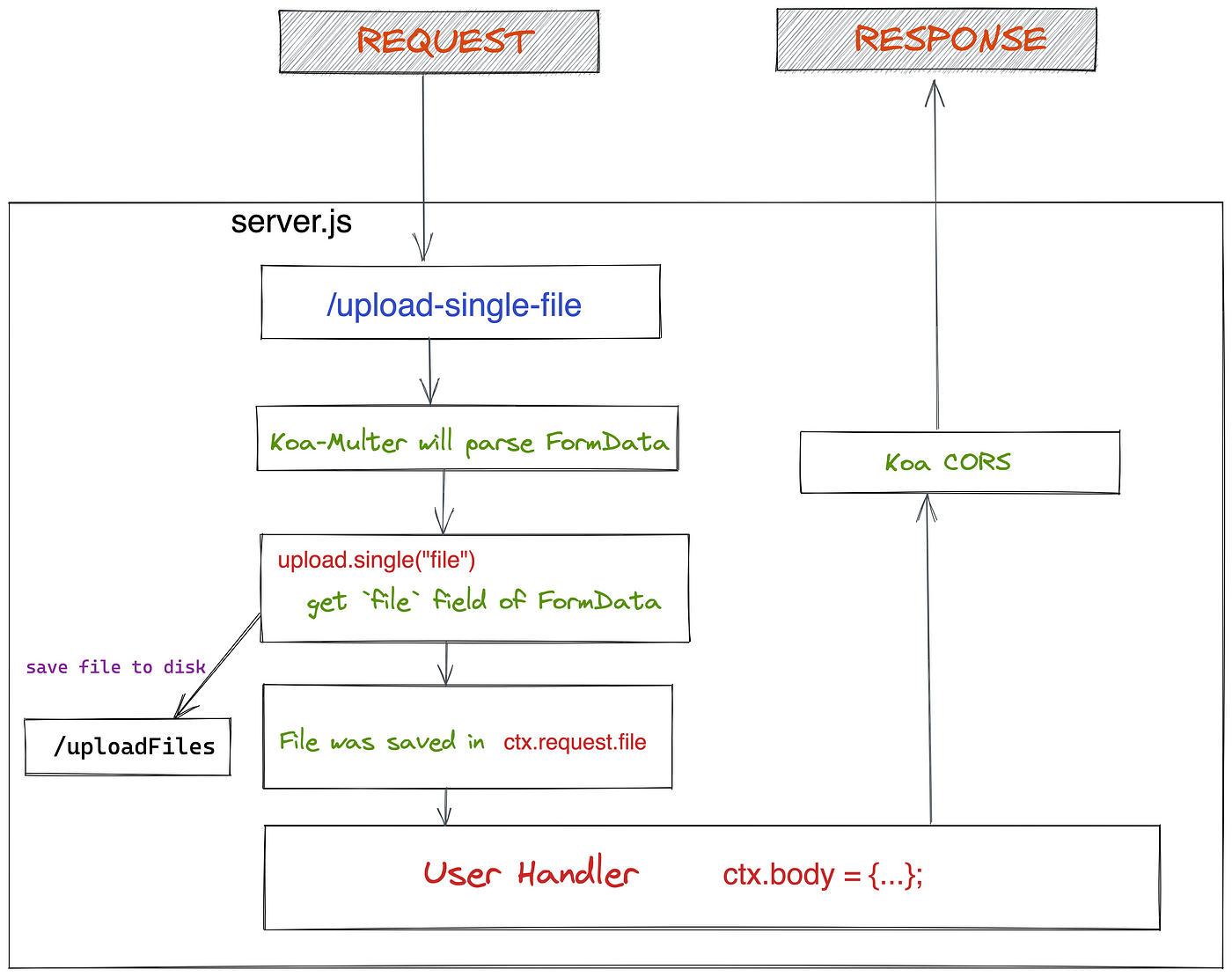
Anyhow, you should try information technology yourself.
Upload multiple files
With the above foundation, it is much simpler for us to write the code for uploading multiple files.
First, nosotros need to modify the input element and add the multiple attribute to it.
<input type="file" id="fileInput" multiple> This is to tell the browser that at present this input element should allow the user to select multiple files at the same time.
Then after the user selects multiple files, the data will be placed in fileElement.files. When we construct formdata, we demand to traverse this list and put all files into formdata.
allow files = Array.from(fileElement.files); let formData = new FormData();
files.forEach((file) => {
formData.append("file", file);
});
Then the code of uploading the file doesn't demand modification.
Hither is the complete code:
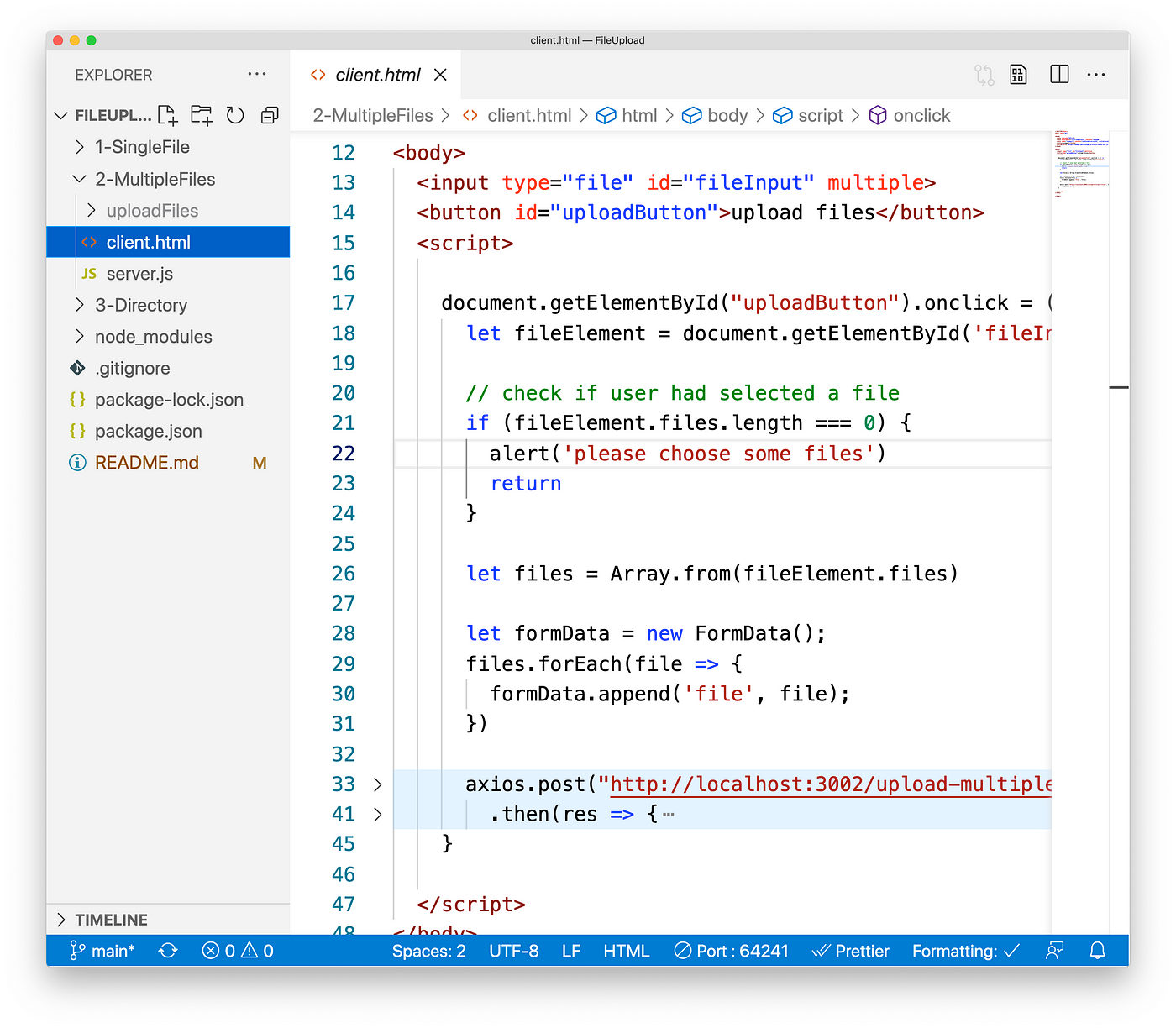
The file is located on ii-MultipleFiles/client.html in the project.
At the aforementioned fourth dimension, nosotros also need to adjust the lawmaking on the server-side.
First, nosotros demand to add the corresponding route /upload-multiple-files
, and then use the upload.fields([{ name: "file" }]) middleware to handle multiple files. Subsequently that, the FormData data in request will be placed in ctx.files.file.
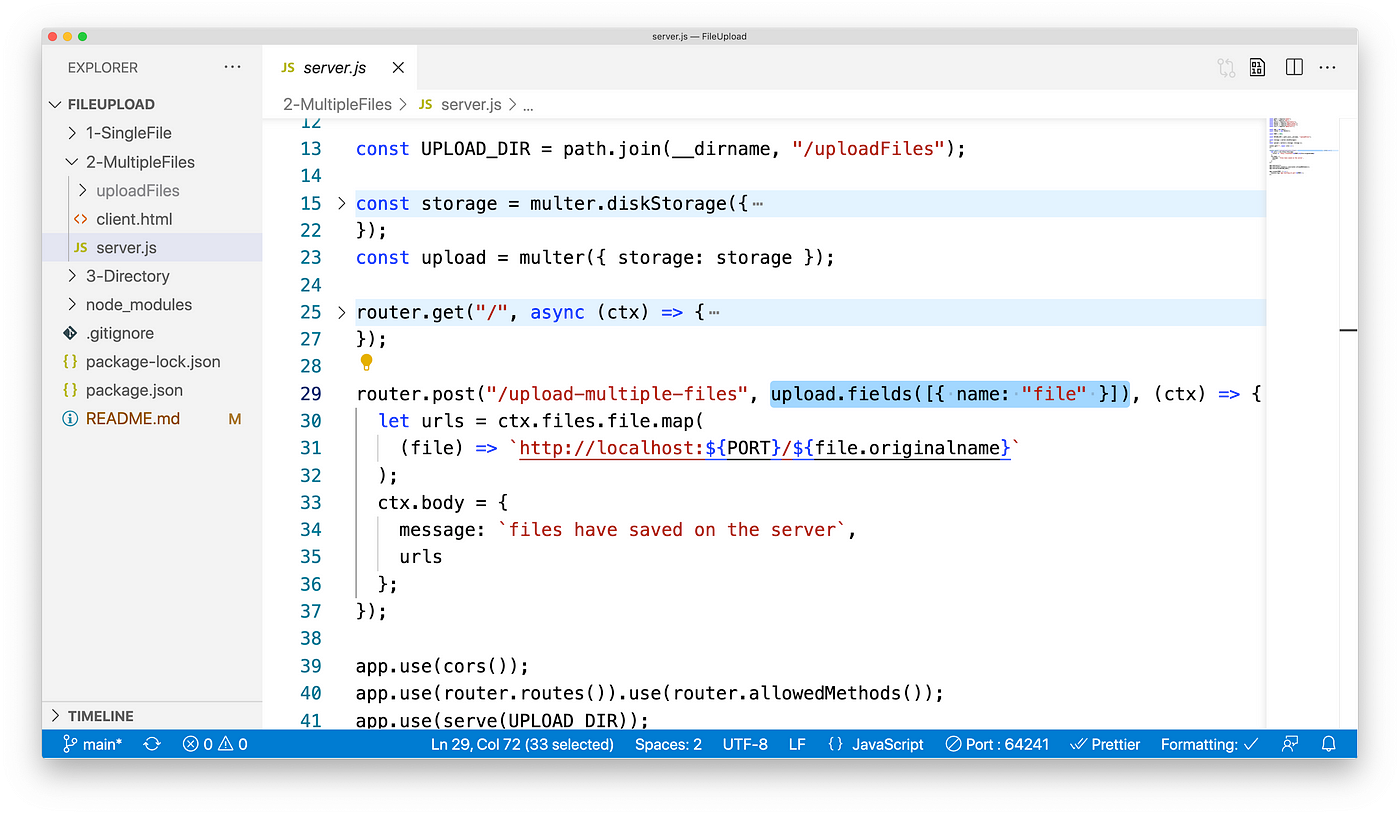
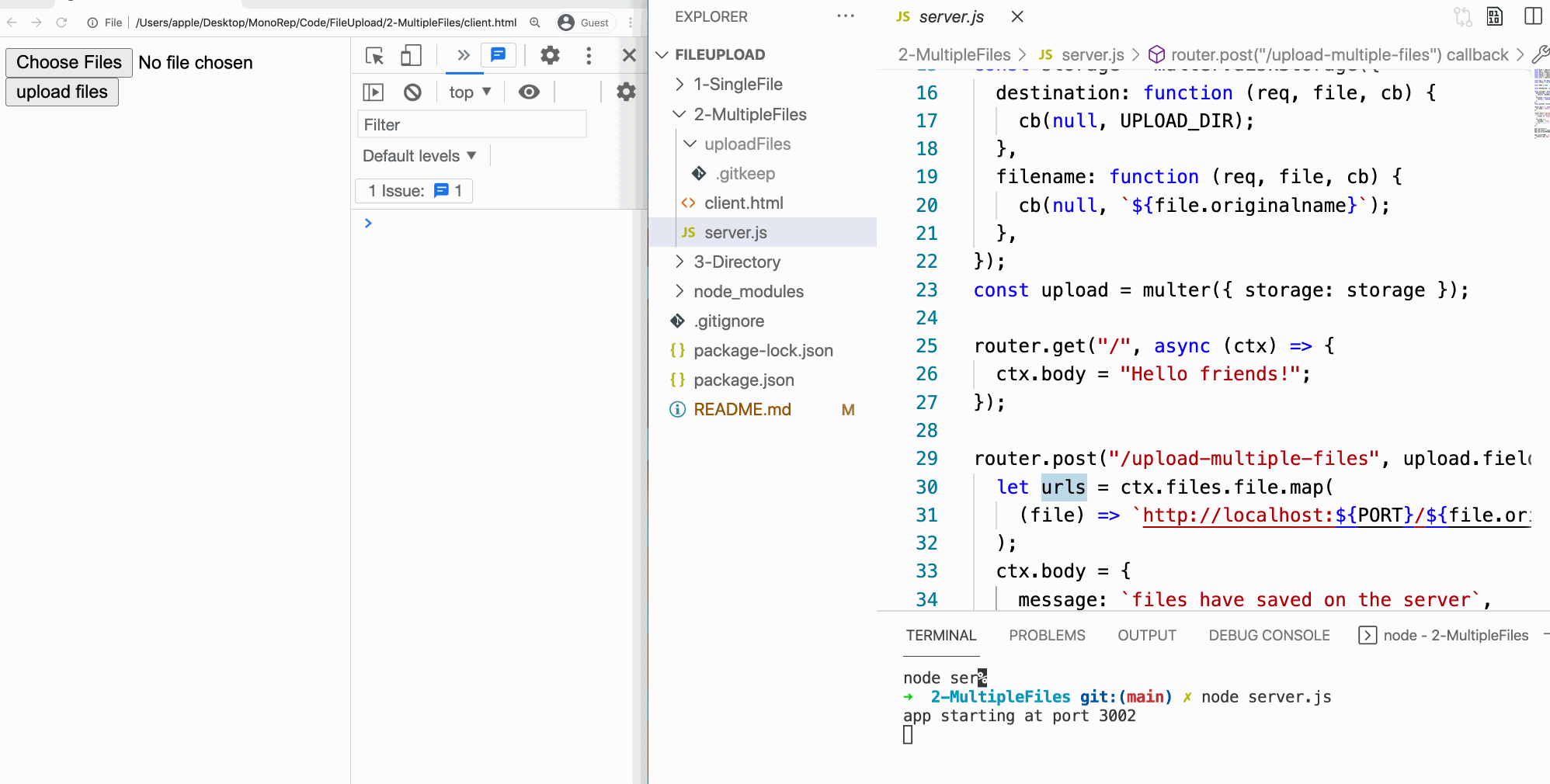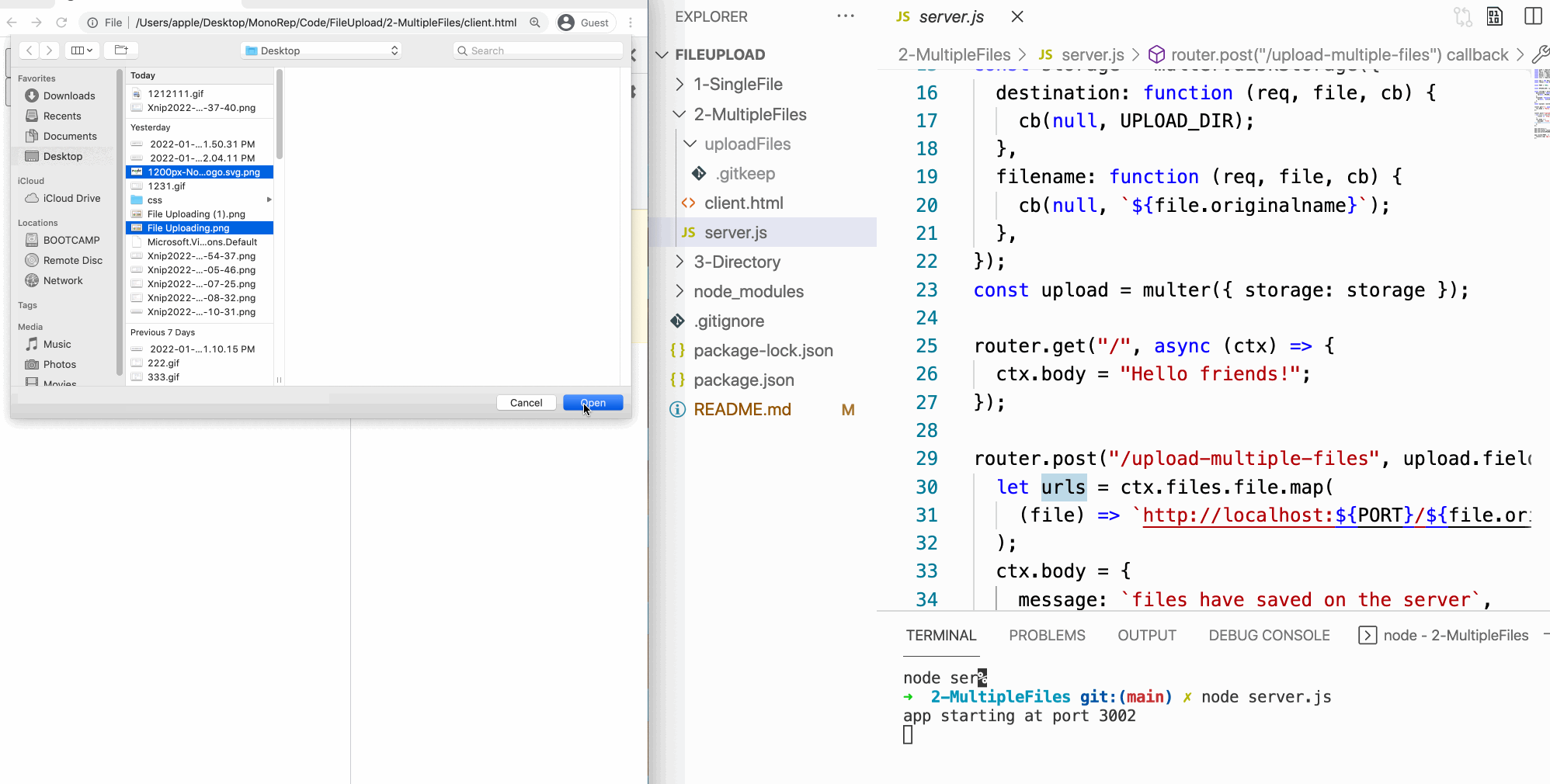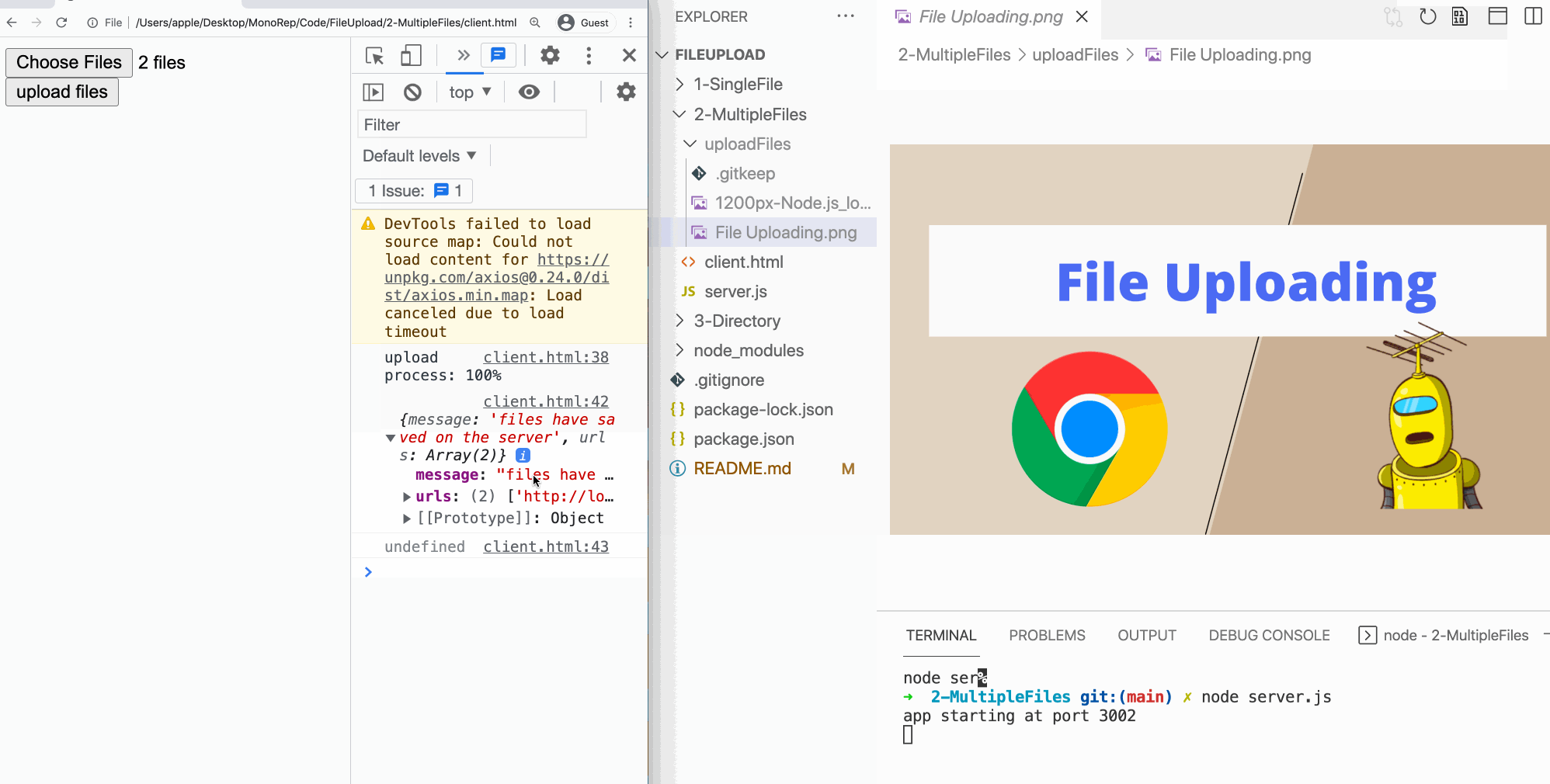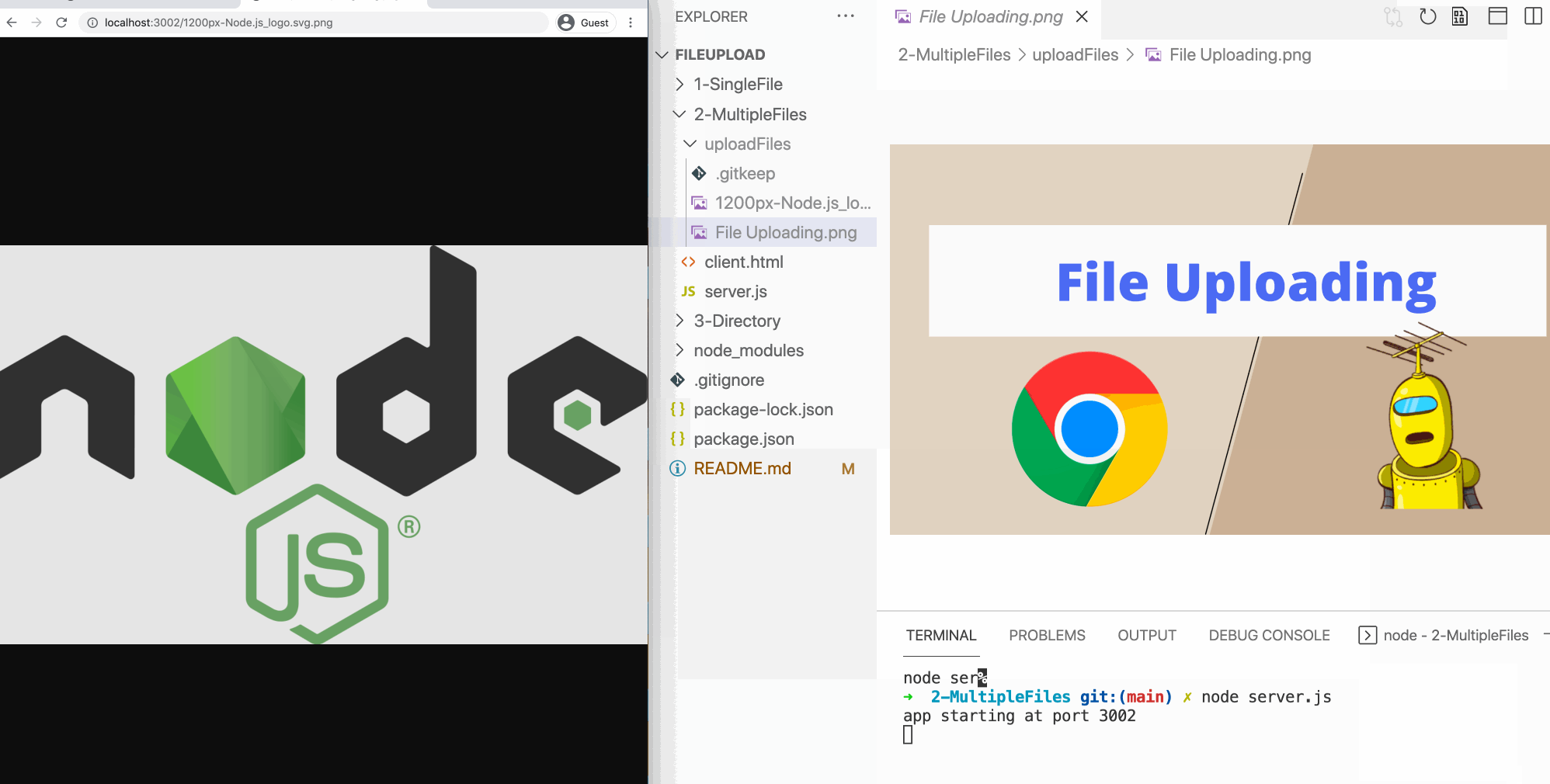
Demo:
Upload directory
Now permit'due south expect at the steps to upload a directory.
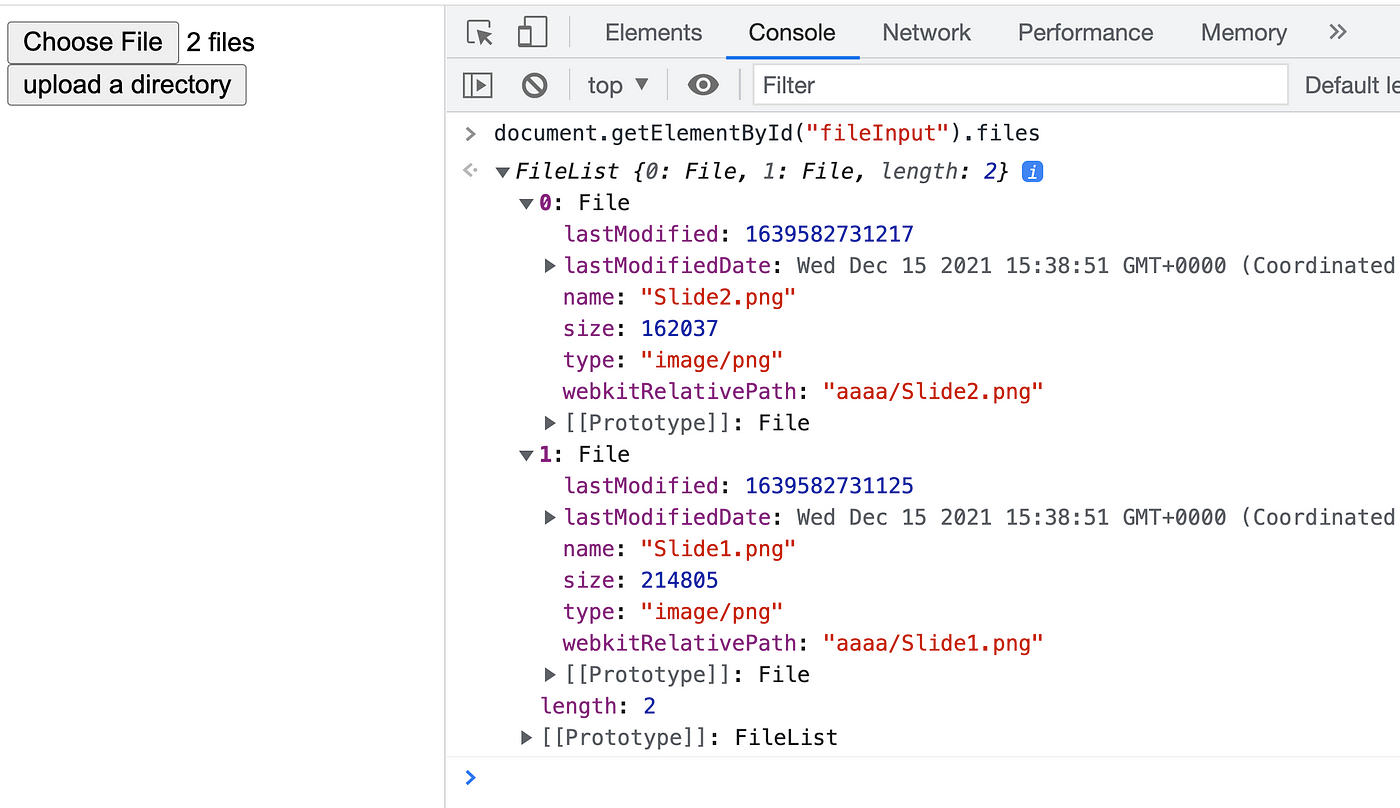
Similarly to before, we need to set the attribute of the input chemical element to this:
<input type="file" id="fileInput" webkitdirectory> So when uploading the directory, the files object of input element volition take the webkitRlativePath belongings, and we will also add them to the formdata
It should be noted here that when the file name contains \, koa-multer may make an fault. To prepare this, nosotros need to replace \ with @ symbol.
formData.append('file', file, file.webkitRelativePath.supersede(/\//g, "@")); 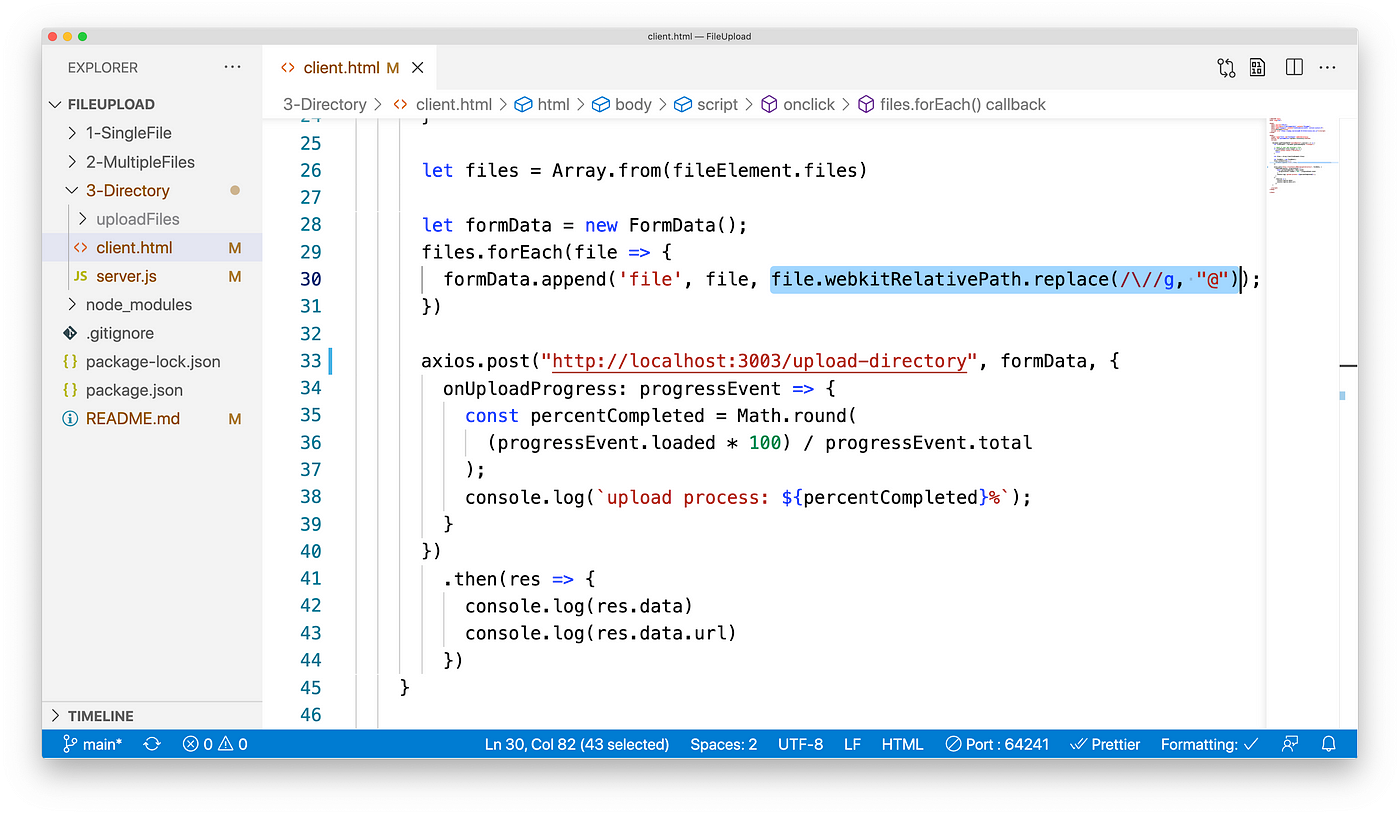
So we also need to modify the respective server code:
Demo:
Conclusion
Well, nosotros have analyzed the process of uploading a unmarried file, multiple files, and directories in plough. Information technology'south actually very simple, just iii steps:
- Using the
inputelement to permit the user select a file - Read the file and construct FormData
- Upload FormData with Axios
All the code is on GitHub, you can endeavour information technology yourself. If you have any questions, you can get out a comment.
Due to the length of the article, the remainder of the file uploading will be included in a after article. If you are interested in this content, yous can follow me.
Thank you for reading.
Source: https://betterprogramming.pub/a-complete-guide-of-file-uploading-in-javascript-2c29c61336f5
0 Response to "How to Put Uploaded Files Into a Folder Javascript"
Post a Comment